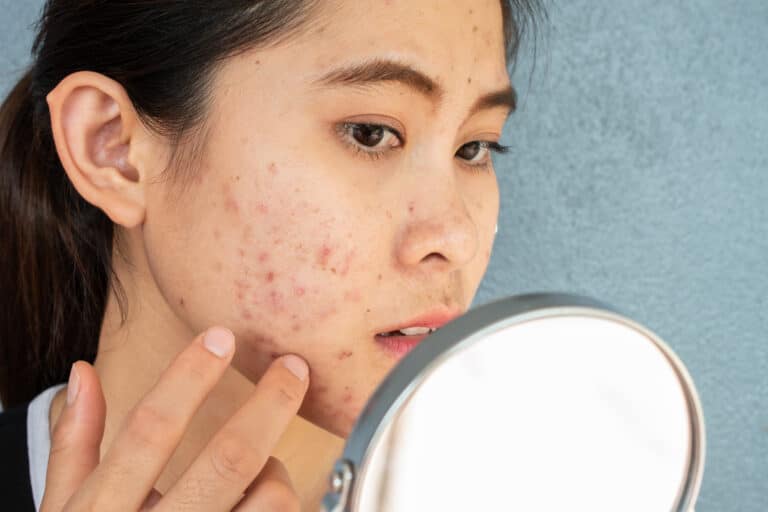
Accutane is a popular acne medication, but how exactly does it work? Are there any side effects and risks? What is Accutane made of? Understanding this drug can help you decide if it’s right for you.
What Is Accutane?
Accutane, now called Zenatane, is an oral medication known as isotretinoin that’s approved to treat severe acne.1 Isotretinoin is a form of retinoid derived from vitamin A and has a long history of use in the United States.2 It remains the gold standard treatment for nodulocystic acne.3
What Does Accutane Do?
Isotretinoin helps improve types of acne that cause deep, painful nodules and cysts and often lead to scars. Physicians prescribe isotretinoin when antibiotics and other treatments do not work.4
The medication blocks oil gland activity and has anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory properties that help to cure acne or produce long-term remission.5 Treatment usually lasts about four to five months but may vary, depending on the individual.6
How Does Accutane Work?
Isotretinoin has many functions and may treat several other skin conditions. Its exact mechanism is unclear, but it’s thought to block sebaceous or oil gland activity and keratinization.7
Keratinization is when skin cells die and become filled with keratin proteins and migrate to the surface of your skin to form part of the skin barrier.8 Isotretinoin also reduces sebum gland size and sebum or oil production.9
Isotretinoin is known as a prodrug because it converts to an active form of vitamin A called all-trans-retinoic acid.10 This chemical binds to retinoic acid receptors inside your cells and normalizes keratinization, protein production, and cell division and renewal.11
Receptor activation also helps suppress sebum or oil production and reduces gland size and activity by 90%. In addition, isotretinoin influences the hair follicle environment, which helps control the bacteria that cause acne.12
Is Accutane Effective?
Isotretinoin is the most effective medication for moderate to severe nodular or cystic acne.13 A meta-analysis of 210 articles with 221 trials and 65,601 patients examined 37 acne interventions, including isotretinoin, topical and oral antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide, and others. The analysis found that isotretinoin was the most effective of all the treatments.14
The medication does produce some reversible side effects. The most common side effect of isotretinoin is dry lips, known as cheilitis, which affects about 90% of people.15 Dry skin and sun sensitivity are other common side effects, along with dry eyes and mouth, itching, hair thinning, infections, irritations, and rashes.16 Overall, isotretinoin is an effective medication and can help cure acne or prompt long-term remission. Severe acne can cause long-lasting physical and psychological effects that impact mental health and self-esteem, making isotretinoin essential. Explore expert articles from My Skin Treatment for more information about acne and effective treatments.
SOURCES:
- LiverTox: “Isotretinoin.”
- Brazilian Society of Dermatology: “Consensus on the use of oral isotretinoin in dermatology.”
- Journal of Drugs in Dermatology: “Self-Reported Long-Term Side Effects of Isotretinoin: A Case Series.”
- American Academy of Dermatology Association: “Isotretinoin: Overview.”
- Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology: “The use of isotretinoin for acne – an update on optimal dosing, surveillance, and adverse effects.”
- American Academy of Dermatology Association: “Isotretinoin: Overview.”
- StatPearls: “Isotretinoin.”
- Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology: “Pathophysiology of keratinization.”
- StatPearls: “Isotretinoin.”
- Brazilian Society of Dermatology: “Consensus on the use of oral isotretinoin in dermatology.”
- Brazilian Society of Dermatology: “Consensus on the use of oral isotretinoin in dermatology.”
- Brazilian Society of Dermatology: “Consensus on the use of oral isotretinoin in dermatology.”
- Annals of Family Medicine: “Comparative Efficacy of Pharmacological Treatments for Acne Vulgaris: A Network Meta-Analysis of 221 Randomized Controlled Trials.”
- Annals of Family Medicine: “Comparative Efficacy of Pharmacological Treatments for Acne Vulgaris: A Network Meta-Analysis of 221 Randomized Controlled Trials.”
- StatPearls: “Isotretinoin.”
- StatPearls: “Isotretinoin.”